티스토리 뷰
Hashing
임의의 길이의 값을 해시함수를 사용하여 고정된 크기의 값으로 변환
Hash Table
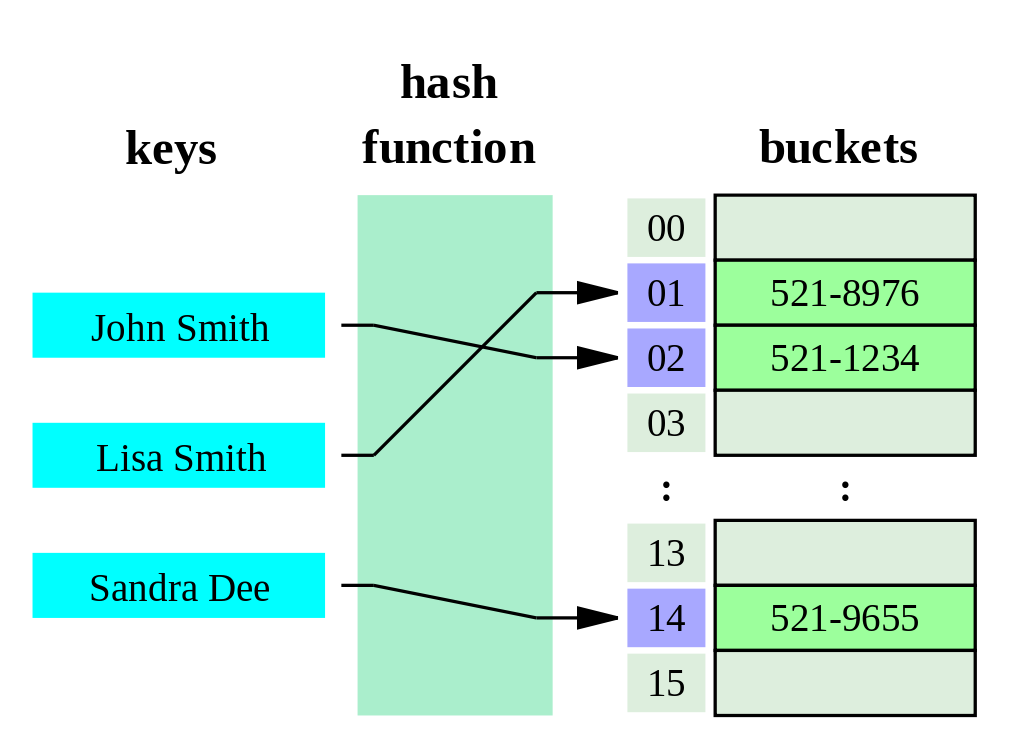
- hash table은 Key, Value로 데이터를 저장하는 자료구조이다
- 검색하고자 하는 Key값을 입력받아, hash함수의 결과물인 hash code를 배열의 index로 Value에 접근
- Time complexity : O(1)
- Key, Hash function, Hash code, Value, Bucket slot으로 이루어져 있음
- Key
‣ Unique value이며 Hash function에 input되는 값이다.
‣ Key는 character, string, number, filedata 등이 올 수 있다.
- Hash function
‣ Key를 입력받아 hash code를 반환함
‣ Key는 길이가 다양하게 입력되지만, Hash function에 input하여 고정된 결과의 반환 하여 효율적인 공간활용이 가능하다.
‣ 다른 Key가 같은 hash가 되는 경우 Hash Collision이 발생하는데, 이를 해결하기 위한 방법으로 Separate Chaining, Open Addressing 2가지가 있다.
- Hash code
‣ Hash function에서 반환하는 값
‣ bucket slot에서 value와 매칭되어 저장됨
- Value
‣ bucket slot에 hash code와 매칭되어 저장됨
‣ 저장, 삭제, 검색, 접근이 가능해야 함
Insert
- Hash function에 argument로 key를 넘겨주고 hash code를 반환 받는다.
- hash code는 unique이다.
- hash code를 인덱스로 하여 value를 저장한다.
- 다른 key가 같은 hash code로 변경되는 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
- Time complexity : O(1) ~ 최악의 경우(충돌이 나는 경우) O(n)
Search
- Key값으로 Hash function을 이용해 hash code를 얻는다.
- hash code로 value에 바로 접근한다.
- Time complexity : O(1)
Delete
- Key값으로 Hash function을 이용해 hash code를 얻는다.
- hash code로 value에 바로 접근한다.
- 해당 hash code와 value를 삭제한다.
- Time complexity : O(1)
Collistion Resolution
- 다른 Key가 같은 hash code가 될 경우 hash 충돌이 일어난다.
1. Separate Chaining
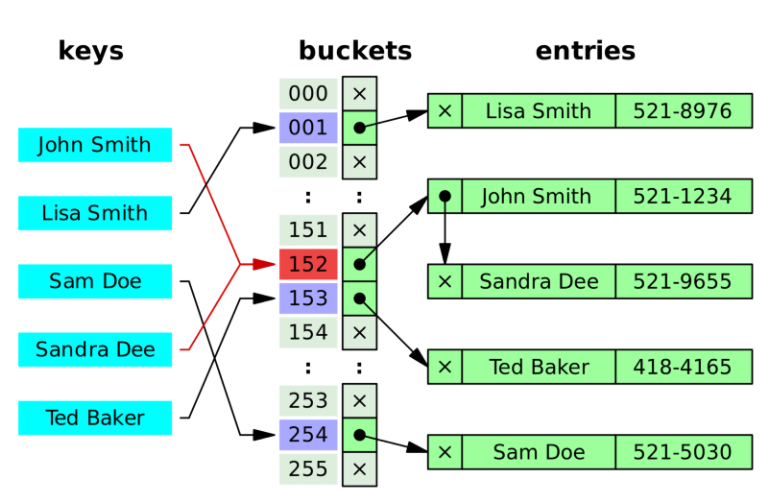
- 충돌이 난 Key에 대하여 기존 Value에 새로운 Value를 연결시키는 방법이다.
- Time complexity : O(nm) (저장소 길이 n, key의 수 m)
- 하나의 hash code에 대한 데이터가 계속 연결된다면 검색/삭제 효율이 낮아지는 단점이있다.
2. Open Addressing

- Liear Probing(선형 탐색) : 해당 hash code 이후의 비어있는 공간에 데이터를 저장한다.
- Quadratic Probing(제곱 탐색) : 해당 hash code의 제곱으로 hash code를 변경하여 저장
- Double Hasing(이중 해싱) : Hash function을 한번 더 실행한 데이터를 저장
- Hash function 의 성능에 따라 HashTable의 성능이 결정된다.
- Time complexity : O(1) ~ O(n)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Node {
private:
string key;
int value;
Node* nextNode;
public:
Node() : key(""), value(0), nextNode(NULL) {}
Node(string _key, int _value) {
key = _key;
value = _value;
nextNode = NULL;
}
Node* getNext() { return nextNode; }
void setNext(Node* next) { nextNode = next; }
string getKey() { return key; }
int getValue() { return value; }
};
class HashTable {
private:
int size;
Node* nodeList;
int hashFunction(string s) {
int len = s.length();
int hash = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
hash += s[i];
}
return hash % size;
}
public:
HashTable(int _size) {
size = _size;
nodeList = new Node[_size];
}
~HashTable() {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* cur = nodeList[i].getNext();
while (cur != NULL) {
Node* temp = cur->getNext();
delete cur;
cur = temp;
}
}
delete[] nodeList;
}
void put(string key, int value) {
int index = hashFunction(key);
Node* next = nodeList[index].getNext();
Node* cur = &nodeList[index];
while (next != NULL) {
cur = next;
next = next->getNext();
}
Node* newNode = new Node(key, value);
cur->setNext(newNode);
}
Node get(string key) {
int index = hashFunction(key);
Node* cur = nodeList[index].getNext();
while (cur != NULL) {
if (!key.compare(cur->getKey())) {
return *cur;
}
cur = cur->getNext();
}
return Node();
}
};'Computer Science > 알고리즘_자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] BST(Binary Search Tree, 이진탐색트리) (0) | 2021.06.17 |
|---|---|
| [알고리즘] 위상 정렬(Topology Sort) (0) | 2021.06.01 |
| [자료구조] Doubly Linked List(2중 연결 리스트) (0) | 2021.05.20 |
| [자료구조] 2진트리 탐색 코드 (0) | 2021.04.20 |
| Big-O Notation (0) | 2021.03.12 |
